算法思想 - 搜索算法
算法思想 - 搜索算法
本文主要介绍算法中搜索算法的思想,主要包含BFS,DFS。
搜索相关题目
深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索广泛运用于树和图中,但是它们的应用远远不止如此。
BFS
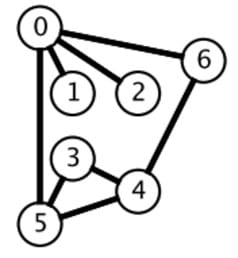
广度优先搜索的搜索过程有点像一层一层地进行遍历,每层遍历都以上一层遍历的结果作为起点,遍历一个距离能访问到的所有节点。需要注意的是,遍历过的节点不能再次被遍历。
第一层:
- 0 -> {6,2,1,5};
第二层:
- 6 ->
- 2 -> {}
- 1 -> {}
- 5 ->
第三层:
- 4 -> {}
- 3 -> {}
可以看到,每一层遍历的节点都与根节点距离相同。设 di 表示第 i 个节点与根节点的距离,推导出一个结论: 对于先遍历的节点 i 与后遍历的节点 j,有 di<=dj。利用这个结论,可以求解最短路径等 最优解 问题: 第一次遍历到目的节点,其所经过的路径为最短路径。应该注意的是,使用 BFS 只能求解无权图的最短路径。
在程序实现 BFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 队列: 用来存储每一轮遍历得到的节点;
- 标记: 对于遍历过的节点,应该将它标记,防止重复遍历。
计算在网格中从原点到特定点的最短路径长度
[[1,1,0,1],
[1,0,1,0],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,0,1,1]]
1 表示可以经过某个位置,求解从 (0, 0) 位置到 (tr, tc) 位置的最短路径长度。
public int minPathLength(int[][] grids, int tr, int tc) {
final int[][] direction = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
final int m = grids.length, n = grids[0].length;
Queue<Pair<Integer, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair<>(0, 0));
int pathLength = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
pathLength++;
while (size-- > 0) {
Pair<Integer, Integer> cur = queue.poll();
for (int[] d : direction) {
int nr = cur.getKey() + d[0], nc = cur.getValue() + d[1];
Pair<Integer, Integer> next = new Pair<>(nr, nc);
if (next.getKey() < 0 || next.getValue() >= m
|| next.getKey() < 0 || next.getValue() >= n) {
continue;
}
grids[next.getKey()][next.getValue()] = 0; // 标记
if (next.getKey() == tr && next.getValue() == tc) {
return pathLength;
}
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
组成整数的最小平方数数量
279. Perfect Squares (Medium)在新窗口打开
For example, given n = 12, return 3 because 12 = 4 + 4 + 4; given n = 13, return 2 because 13 = 4 + 9.
可以将每个整数看成图中的一个节点,如果两个整数之差为一个平方数,那么这两个整数所在的节点就有一条边。
要求解最小的平方数数量,就是求解从节点 n 到节点 0 的最短路径。
本题也可以用动态规划求解,在之后动态规划部分中会再次出现。
public int numSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> squares = generateSquares(n);
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] marked = new boolean[n + 1];
queue.add(n);
marked[n] = true;
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
level++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (int s : squares) {
int next = cur - s;
if (next < 0) {
break;
}
if (next == 0) {
return level;
}
if (marked[next]) {
continue;
}
marked[next] = true;
queue.add(cur - s);
}
}
}
return n;
}
/**
* 生成小于 n 的平方数序列
* @return 1,4,9,...
*/
private List<Integer> generateSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> squares = new ArrayList<>();
int square = 1;
int diff = 3;
while (square <= n) {
squares.add(square);
square += diff;
diff += 2;
}
return squares;
}
最短单词路径
127. Word Ladder (Medium)在新窗口打开
Input:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Output: 5
Explanation: As one shortest transformation is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
return its length 5.
Input:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Output: 0
Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore no possible transformation.
找出一条从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短路径,每次移动规定为改变一个字符,并且改变之后的字符串必须在 wordList 中。
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
wordList.add(beginWord);
int N = wordList.size();
int start = N - 1;
int end = 0;
while (end < N && !wordList.get(end).equals(endWord)) {
end++;
}
if (end == N) {
return 0;
}
List<Integer>[] graphic = buildGraphic(wordList);
return getShortestPath(graphic, start, end);
}
private List<Integer>[] buildGraphic(List<String> wordList) {
int N = wordList.size();
List<Integer>[] graphic = new List[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
graphic[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (isConnect(wordList.get(i), wordList.get(j))) {
graphic[i].add(j);
}
}
}
return graphic;
}
private boolean isConnect(String s1, String s2) {
int diffCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length() && diffCnt <= 1; i++) {
if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) {
diffCnt++;
}
}
return diffCnt == 1;
}
private int getShortestPath(List<Integer>[] graphic, int start, int end) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] marked = new boolean[graphic.length];
queue.add(start);
marked[start] = true;
int path = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
path++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (int next : graphic[cur]) {
if (next == end) {
return path;
}
if (marked[next]) {
continue;
}
marked[next] = true;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
DFS
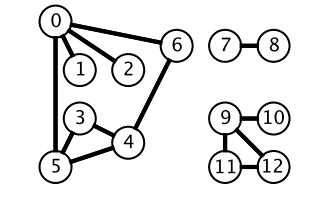
广度优先搜索一层一层遍历,每一层得到的所有新节点,要用队列存储起来以备下一层遍历的时候再遍历。
而深度优先搜索在得到一个新节点时立马对新节点进行遍历: 从节点 0 出发开始遍历,得到到新节点 6 时,立马对新节点 6 进行遍历,得到新节点 4;如此反复以这种方式遍历新节点,直到没有新节点了,此时返回。返回到根节点 0 的情况是,继续对根节点 0 进行遍历,得到新节点 2,然后继续以上步骤。
从一个节点出发,使用 DFS 对一个图进行遍历时,能够遍历到的节点都是从初始节点可达的,DFS 常用来求解这种 可达性 问题。
在程序实现 DFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 栈: 用栈来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归栈。
- 标记: 和 BFS 一样同样需要对已经遍历过的节点进行标记。
查找最大的连通面积
695. Max Area of Island (Easy)在新窗口打开
[[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
private int m, n;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, dfs(grid, i, j));
}
}
return maxArea;
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || grid[r][c] == 0) {
return 0;
}
grid[r][c] = 0;
int area = 1;
for (int[] d : direction) {
area += dfs(grid, r + d[0], c + d[1]);
}
return area;
}
矩阵中的连通分量数目
200. Number of Islands (Medium)在新窗口打开
Input:
11000
11000
00100
00011
Output: 3
可以将矩阵表示看成一张有向图。
private int m, n;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
int islandsNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] != '0') {
dfs(grid, i, j);
islandsNum++;
}
}
}
return islandsNum;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || grid[i][j] == '0') {
return;
}
grid[i][j] = '0';
for (int[] d : direction) {
dfs(grid, i + d[0], j + d[1]);
}
}
好友关系的连通分量数目
547. Friend Circles (Medium)在新窗口打开
Input:
[[1,1,0],
[1,1,0],
[0,0,1]]
Output: 2
Explanation:The 0th and 1st students are direct friends, so they are in a friend circle.
The 2nd student himself is in a friend circle. So return 2.
好友关系可以看成是一个无向图,例如第 0 个人与第 1 个人是好友,那么 M[0][1] 和 M[1][0] 的值都为 1。
private int n;
public int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
n = M.length;
int circleNum = 0;
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!hasVisited[i]) {
dfs(M, i, hasVisited);
circleNum++;
}
}
return circleNum;
}
private void dfs(int[][] M, int i, boolean[] hasVisited) {
hasVisited[i] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
if (M[i][k] == 1 && !hasVisited[k]) {
dfs(M, k, hasVisited);
}
}
}
填充封闭区域
130. Surrounded Regions (Medium)在新窗口打开
For example,
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
After running your function, the board should be:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
使被 'X' 包围的 'O' 转换为 'X'。
先填充最外侧,剩下的就是里侧了。
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
private int m, n;
public void solve(char[][] board) {
if (board == null || board.length == 0) {
return;
}
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(board, i, 0);
dfs(board, i, n - 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(board, 0, i);
dfs(board, m - 1, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'T') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
} else if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
private void dfs(char[][] board, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || board[r][c] != 'O') {
return;
}
board[r][c] = 'T';
for (int[] d : direction) {
dfs(board, r + d[0], c + d[1]);
}
}
能到达的太平洋和大西洋的区域
417. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow (Medium)在新窗口打开
Given the following 5x5 matrix:
Pacific ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *
~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *
~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 *
~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *
~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *
* * * * * Atlantic
Return:
[[0, 4], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 2], [3, 0], [3, 1], [4, 0]] (positions with parentheses in above matrix).
左边和上边是太平洋,右边和下边是大西洋,内部的数字代表海拔,海拔高的地方的水能够流到低的地方,求解水能够流到太平洋和大西洋的所有位置。
private int m, n;
private int[][] matrix;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public List<int[]> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {
List<int[]> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {
return ret;
}
m = matrix.length;
n = matrix[0].length;
this.matrix = matrix;
boolean[][] canReachP = new boolean[m][n];
boolean[][] canReachA = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(i, 0, canReachP);
dfs(i, n - 1, canReachA);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(0, i, canReachP);
dfs(m - 1, i, canReachA);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (canReachP[i][j] && canReachA[i][j]) {
ret.add(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
return ret;
}
private void dfs(int r, int c, boolean[][] canReach) {
if (canReach[r][c]) {
return;
}
canReach[r][c] = true;
for (int[] d : direction) {
int nextR = d[0] + r;
int nextC = d[1] + c;
if (nextR < 0 || nextR >= m || nextC < 0 || nextC >= n
|| matrix[r][c] > matrix[nextR][nextC]) {
continue;
}
dfs(nextR, nextC, canReach);
}
}